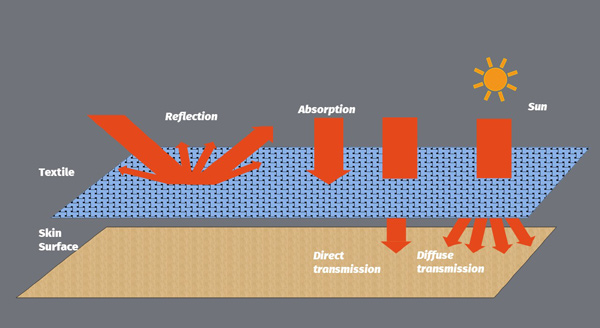
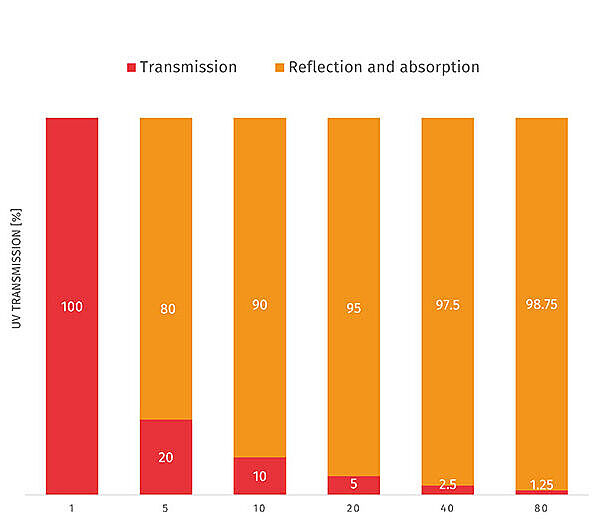
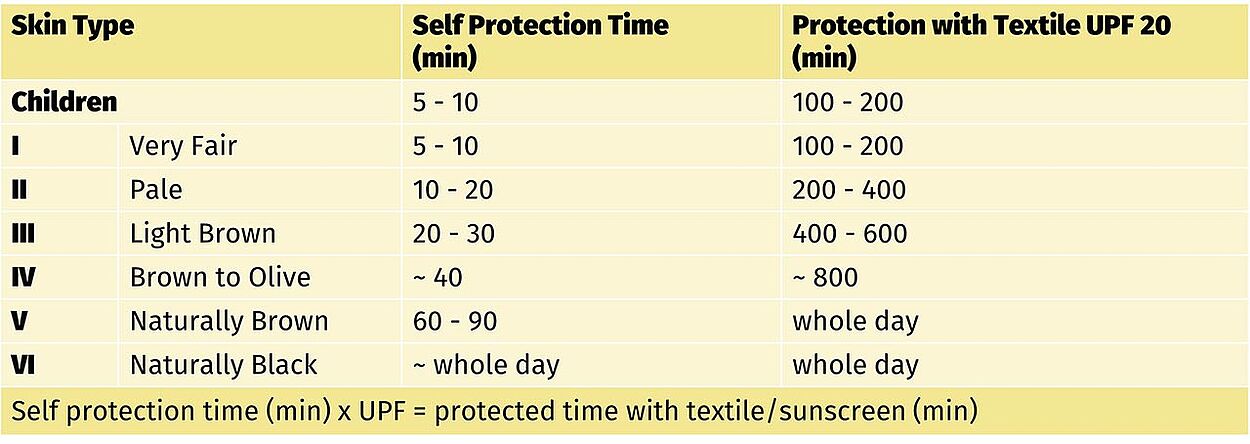
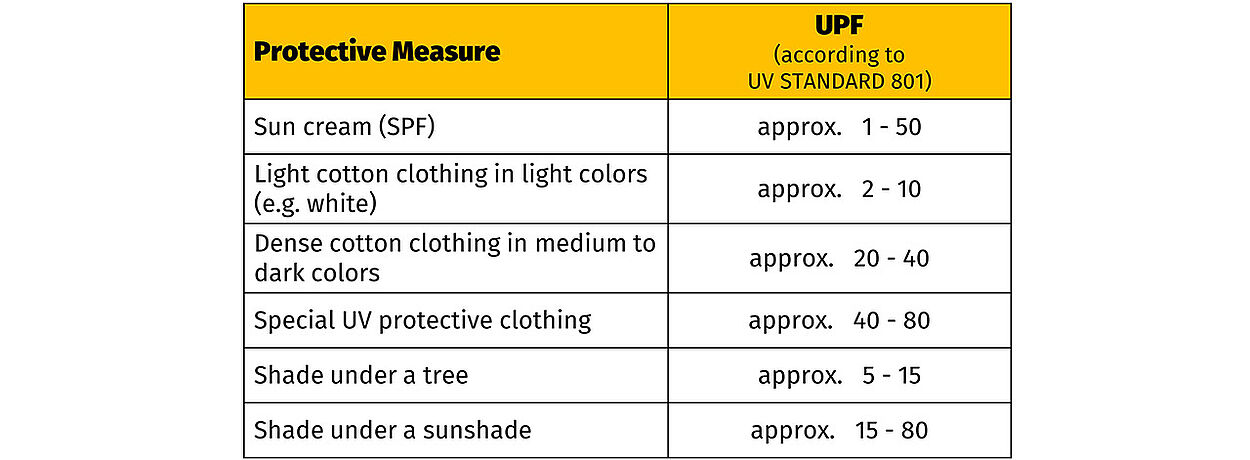
UV Standard for Testing for Use Situations
For the UV STANDARD 801, we consider important aspects of use, including stretching of the textile, wetting of clothing, weathering of shading textiles, aging by certain abrasion and washing cycles and many more. We also assume maximum radiation intensity with the solar spectrum in Melbourne, Australia on January 1st (peak of the Australian summer).